NESS Documentation v1.1.1
2 NESS Overview
2.8 Settings
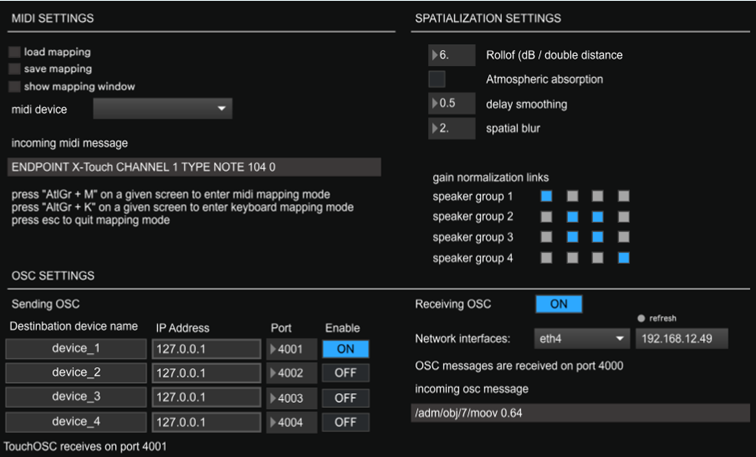
Midi settings
Most of the UI controls can be mapped to a midi controller.
The UI supports midi learn from any
midi device
- Press AltGr + M on a given screen of the application to map a control to a midi controller
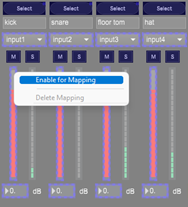
- Click on the control to map and click on “Enable for mapping”
- Use the controller button that must be associated to the UI control
- Press Escape to quit the mapping mode
- Press AltGr + k on a given screen of the application to map a control to a keyboard key
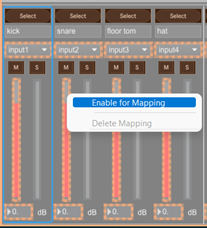
Click on the control to map and click on “Enable for mapping”
Press a key on the keyboard to assign it to the UI control
Press Escape to quit the mapping mode
| Load mapping |
|
| Save mapping |
|
| Show mapping window |
|
| Midi device |
|
| Incoming midi message |
|
OSC Settings
NESS can be controlled with the OSC protocol with the TouchOSC application and the available here .
NESS also supports the ADM OSC protocol for the control of the sources
NESS receives osc messages on the port 4000
When the TouchOSC app is connected to NESS The message « TouchOSC connected » is displayed in green
| OSC Settings | |
| Network interface |
|
Nota : this requires Java runtime engine to be installed
| OSC Settings | |
| Incoming OSC message |
|
| Sender |
|
| IP address |
|
| Port |
|
Spatialization Settings
Rollof (dB/ double distance): sets the level decrease law for the acoustic model of the DBAP. 6 dB is a usual value to simulate the acoustic propagation in an outdoor space. A lower value can be used to simulate the sound propagation in an indoor place. A higher value can enhance the distance effect, less speakers will play the sound at the same time, which can enhance the precision of the spatialization for small 360° setups
Atmospheric Absorption : activates or deactivates the high frequency attenuation depending on the distance.
Delay smoothing : smoothing coefficient for the delays. For sources with quick movements, this can create unwanted doppler effect (frequency transposition). The delays are interpolated and smoothed to avoid high pitch transitions. By increasing the value, the transitions are smoothed, but the delays will be less corelated to the source position, which can results in a slightly less precise localization.